Photo ©2005 Paul Hebert
Click photo for a larger image
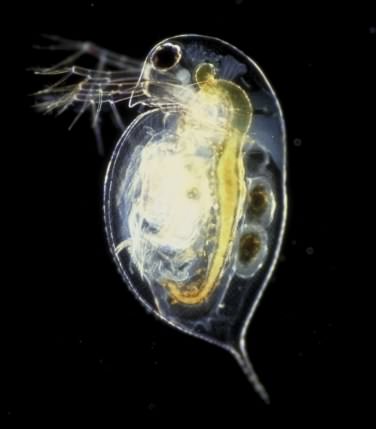
Water Flea - Daphnia Pulex
Family - Daphniidae

Photo ©2005 Paul Hebert
Click photo for a larger image
Water fleas are Crustaceans, of the order Cladocerand. Common in fresh water, there are about 80 different species in the UK, ranging in size from several hundred microns to more than five millimeters (0.007in–0.2in) for the larger species. Daphnia pulex is probably the most common of the water flea species and can be found in most eutrophic waters with an almost world wide distribution. They reproduce in the warmer summer months mostly by parthenogenetic reproduction and will be all female. However when populations are under stress, Eg. drying up of a pond, some of the eggs develop into smaller males, capable of fertilising the eggs, this can also happen at the end of the breeding season developing into "winter eggs" which have the ability to over winter. These eggs can remain at this stage of dormancy for possibly up to twenty years, until the aquatic conditions become more favorable. The body of a water flea is formed by a shell that creates an opening in the underside, this shell or carapace does not grow and they are forced to moult the shell as the animal grows. They eat small organisms and water borne particulates, themselves becoming food for higher organisms, ie. fish. The can be found in almost any water body from small isolated wheel tracks, rain forest tree moss, open freshwater, ponds and puddles.
Several populations of water flea species are considered threatened with the following being listed as vulnerable by IUCN – D. nivalis, D. occidentalis, D. coronata, and D. jollyi. Daphnia are sometimes used to clear fish tanks of algae due to their diet of bacteria, small algae particles and detritus. Some algae is not eaten by Daphnia, blue–green algae has an outer cell wall that is too tough for Daphnia, and filamentous green algae can be detrimental to the organism's health. Most species of Daphnia including D. pulex are herbivorous or detritivorous, a few are carnivorous and prey on other water fleas.
Site design ©1999– Brickfields Country Park - Privacy -